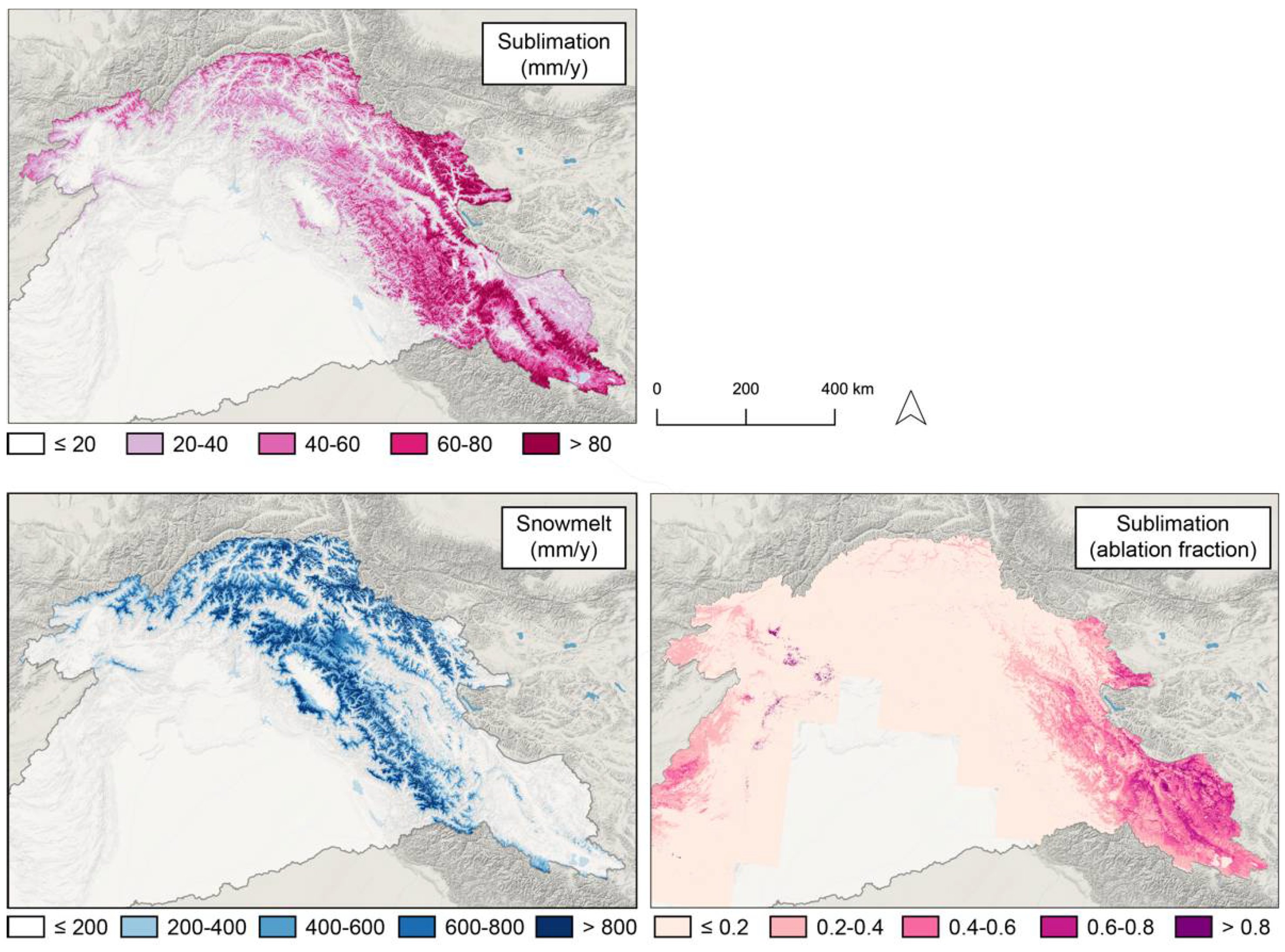
Snowmelt and snow sublimation in the Indus basin
The Indus basin has one of the largest irrigation system in the world. Available water resources are abstracted almost entirely, mostly for crop irrigation in Pakistan.
The Indus basin is also considered as one of the large basins in Asia with the highest dependence on snowmelt runoff.

The contribution of snow and ice melt to runoff in the Indus basin was already well studied [1,2,3] but a pending question was how much water is lost by sublimation of the snow cover in the high mountain regions of the basin?
I used the recent High Mountain Asia snow reanalysis to re-evaluate snowmelt and estimate snow sublimation at the scale of the Indus basin.
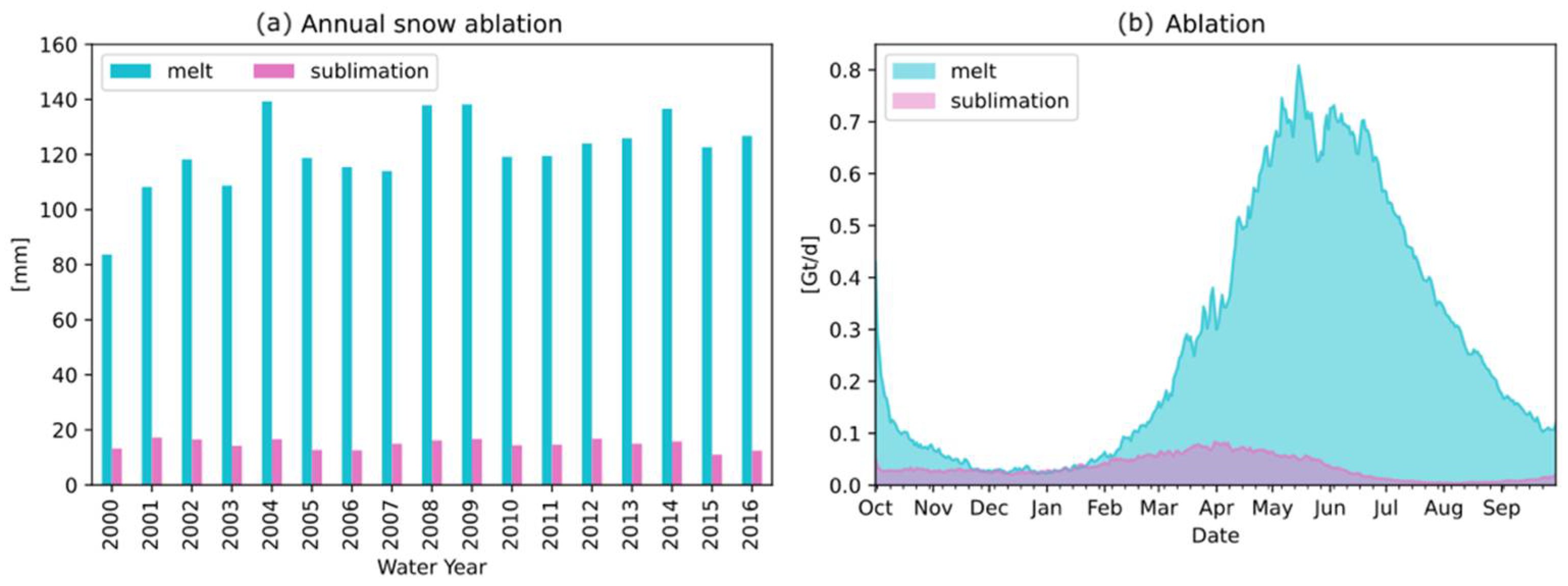
Over 2000–2016, snowmelt was about 25–30% of basin-average annual precipitation. About 11% of the snowfall was « lost » by sublimation, but with a large spatial variability across the basin. Sublimation fraction can be much higher in the arid regions in Ladakh and Western Tibet.
For this study I challenged myself to follow best practices in open science. I only used open data and the code to reproduce the study is available online. It was fun!
Paper: mdpi.com/2073-4441/13/1
Dataset: nsidc.org/data/HMA_SR_D/
Code: https://github.com/sgascoin/HMA-Snow-Reanalysis-scripts/
Many thanks to the authors High Mountain Asia snow reanalysis for sharing this amazing dataset!
Top picture: Mountains in Swat Valley Pakistan (by Designer429, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons)